Distribution and environment of Ascophyllum nodosum
Ascophyllum nodosum is distributed in the cold waters of high latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, mainly concentrated in the sheltered rocky coastlines of the middle intertidal zone along the North Atlantic coast. At high tide, they are exposed to cold, salty water, and at low tide they are exposed to dry, hot sand. The temperature of the living environment varies by more than 20 degrees Celsius in a day and more than 50 degrees Celsius in a year. The harsh environmental changes have allowed the ascophyllum nodosum to evolve a strong vitality of the organization, obtain a strong stress resistance, enrichment and absorption capacity, is recognized in the world for the production of seaweed fertilizer of the best quality raw materials.
Distribution and environment of Ascophyllum nodosum
Ascophyllum nodosum is distributed in the cold waters of high latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, mainly concentrated in the sheltered rocky coastlines of the middle intertidal zone along the North Atlantic coast. At high tide, they are exposed to cold, salty water, and at low tide they are exposed to dry, hot sand. The temperature of the living environment varies by more than 20 degrees Celsius in a day and more than 50 degrees Celsius in a year. The harsh environmental changes have allowed the ascophyllum nodosum to evolve a strong vitality of the organization, obtain a strong stress resistance, enrichment and absorption capacity, is recognized in the world for the production of seaweed fertilizer of the best quality raw materials.
Distribution and environment of Ascophyllum nodosum
Ascophyllum nodosum is distributed in the cold waters of high latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, mainly concentrated in the sheltered rocky coastlines of the middle intertidal zone along the North Atlantic coast. At high tide, they are exposed to cold, salty water, and at low tide they are exposed to dry, hot sand. The temperature of the living environment varies by more than 20 degrees Celsius in a day and more than 50 degrees Celsius in a year. The harsh environmental changes have allowed the ascophyllum nodosum to evolve a strong vitality of the organization, obtain a strong stress resistance, enrichment and absorption capacity, is recognized in the world for the production of seaweed fertilizer of the best quality raw materials.
NMBO'S Ascophyllum Nodosum
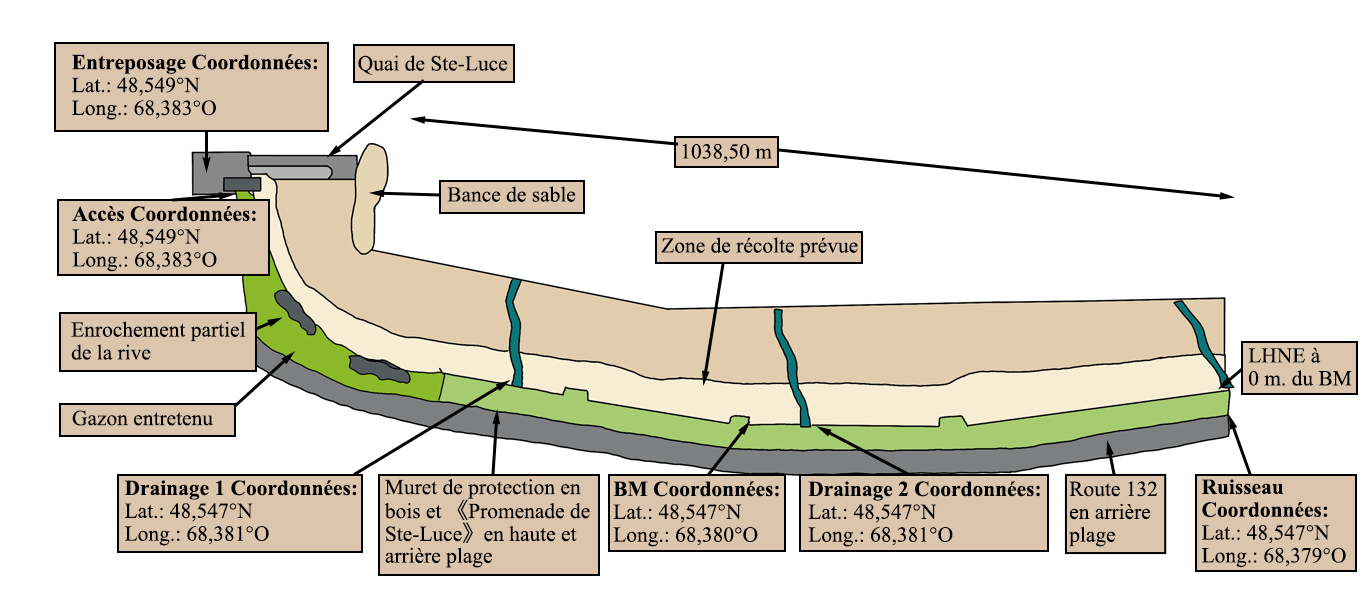
NMBO is with a number of high-quality raw material partners, it has 21 acanthophyllum sea areas in the core sea area of Quebec, Canada, and has obtained long-term seaweed mining permits, with an annual output of 35,000 tons of dry wild ascophyllum nodosum
NMBO'S Ascophyllum Nodosum
NMBO is with a number of high-quality raw material partners, it has 21 acanthophyllum sea areas in the core sea area of Quebec, Canada, and has obtained long-term seaweed mining permits, with an annual output of 35,000 tons of dry wild ascophyllum nodosum

NMBO'S Ascophyllum Nodosum
NMBO is with a number of high-quality raw material partners, it has 21 acanthophyllum sea areas in the core sea area of Quebec, Canada, and has obtained long-term seaweed mining permits, with an annual output of 35,000 tons of dry wild ascophyllum nodosum

The maximum alginic acid content is close to 30%
- Small molecules of alginic acid can stimulate plants to produce IAA, promote rooting, and induce plant self-defense
- Macromolecular alginic acid can improve soil water holding capacity, dilute soil solution salt, and enhance soil buffering capacity
- Alginic acid can preferentially bind with soil heavy metal ions to reduce nutrient loss and improve nutrient absorption efficiency
- As a high-quality carbon source, it can provide a material basis for soil microbial growth, stimulate microbial metabolism, and improve soil microecology
The maximum alginic acid content is close to 30%
- Small molecules of alginic acid can stimulate plants to produce IAA, promote rooting, and induce plant self-defense
- Macromolecular alginic acid can improve soil water holding capacity, dilute soil solution salt, and enhance soil buffering capacity
- Alginic acid can preferentially bind with soil heavy metal ions to reduce nutrient loss and improve nutrient absorption efficiency
- As a high-quality carbon source, it can provide a material basis for soil microbial growth, stimulate microbial metabolism, and improve soil microecology
The maximum alginic acid content is close to 30%
- Small molecules of alginic acid can stimulate plants to produce IAA, promote rooting, and induce plant self-defense
- Macromolecular alginic acid can improve soil water holding capacity, dilute soil solution salt, and enhance soil buffering capacity
- Alginic acid can preferentially bind with soil heavy metal ions to reduce nutrient loss and improve nutrient absorption efficiency
- As a high-quality carbon source, it can provide a material basis for soil microbial growth, stimulate microbial metabolism, and improve soil microecology
IAA (ng/g) Indole Acetic Acid (Auxin) | GA3 (ng/g) Gibberellin | ZT (ng/g) Zeatin (Cytokinin) | |
Dry small kelp | 147.94 | 13.54 | 19.77 |
Dry great kelp | 30.9 | 21.54 | 54.97 |
Ascophyllum nodosum | 594.22 | 46.7 | 87.94 |
Fresh Sargasso | 15.23 | 40 | 83.12 |
Fresh small kelp | 20.53 | 33.96 | 93.95 |
The maximum polysaccharide content of fucoite was close to 20%
- The polysaccharide of fucoite has a direct effect on the adaptation of algae to ultraviolet, dry and high salt environment in tidal zone, and can protect the cell tissue.
- Algae polysaccharides can stimulate the expression of plant salicylic acid channels and synthesize more antibacterial, antiviral and stress-resistant proteins.
IAA (ng/g) Indole Acetic Acid (Auxin) | GA3 (ng/g) Gibberellin | ZT (ng/g) Zeatin (Cytokinin) | |
Dry small kelp | 147.94 | 13.54 | 19.77 |
Dry great kelp | 30.9 | 21.54 | 54.97 |
Ascophyllum nodosum | 594.22 | 46.7 | 87.94 |
Fresh Sargasso | 15.23 | 40 | 83.12 |
Fresh small kelp | 20.53 | 33.96 | 93.95 |
The maximum polysaccharide content of fucoite was close to 20%
- The polysaccharide of fucoite has a direct effect on the adaptation of algae to ultraviolet, dry and high salt environment in tidal zone, and can protect the cell tissue.
- Algae polysaccharides can stimulate the expression of plant salicylic acid channels and synthesize more antibacterial, antiviral and stress-resistant proteins.
The maximum polysaccharide content of fucoite was close to 20%
- The polysaccharide of fucoite has a direct effect on the adaptation of algae to ultraviolet, dry and high salt environment in tidal zone, and can protect the cell tissue.
- Algae polysaccharides can stimulate the expression of plant salicylic acid channels and synthesize more antibacterial, antiviral and stress-resistant proteins.
The maximum polyphenol content of brown algae was close to 15%
- It has significant antioxidant properties and improves the adaptability of tissues to adversity
- It has a unique odor, spectral repellent function, and is not easy to produce tolerance.
Alginic Acid | Fucoidan | Phlorotannin | |
Laminaria japonica | 22.54 | 0.5425 | 3.03 |
Sargassum pallidun | 17.38 | 13.93 | 0.3 |
Macrocystis pyrifera | 27.58 | 10.5 | 1.5 |
Ascophyllum nodosum | 25.76 | 14.175 | 14 |
Enteromorpha prolifra | 0 | 0 | 0 |
The maximum polyphenol content of brown algae was close to 15%
- It has significant antioxidant properties and improves the adaptability of tissues to adversity
- It has a unique odor, spectral repellent function, and is not easy to produce tolerance.
Alginic Acid | Fucoidan | Phlorotannin | |
Laminaria japonica | 22.54 | 0.5425 | 3.03 |
Sargassum pallidun | 17.38 | 13.93 | 0.3 |
Macrocystis pyrifera | 27.58 | 10.5 | 1.5 |
Ascophyllum nodosum | 25.76 | 14.175 | 14 |
Enteromorpha prolifra | 0 | 0 | 0 |
The maximum polyphenol content of brown algae was close to 15%
- It has significant antioxidant properties and improves the adaptability of tissues to adversity
- It has a unique odor, spectral repellent function, and is not easy to produce tolerance.
Other ingredients
- Betaine: increase the content of plant chlorophyll, improve photosynthesis; Maintain water balance and improve crop stress resistance.
- Plant endogenous hormones: can promote cell division and growth, tissue differentiation, induce defense and stress response; Regulate cell osmotic pressure, promote plant growth, improve yield and quality.
Other ingredients
- Betaine: increase the content of plant chlorophyll, improve photosynthesis; Maintain water balance and improve crop stress resistance.
- Plant endogenous hormones: can promote cell division and growth, tissue differentiation, induce defense and stress response; Regulate cell osmotic pressure, promote plant growth, improve yield and quality.
Other ingredients
- Betaine: increase the content of plant chlorophyll, improve photosynthesis; Maintain water balance and improve crop stress resistance.
- Plant endogenous hormones: can promote cell division and growth, tissue differentiation, induce defense and stress response; Regulate cell osmotic pressure, promote plant growth, improve yield and quality.

