Benefits of using seaweed fertilizer for foliar fertilization
Benefits of using seaweed fertilizer for foliar fertilization
Benefits of using seaweed fertilizer for foliar fertilization
① Fast nutrient absorption, good fertilizer effect. After soil fertilization, various nutrient elements are first adsorbed by the soil, and some fertilizers must be absorbed by crop roots through ion exchange or diffusion after a transformation process in the soil, and reach the leaves through the vascular bundles of roots and stems, in which the nutrient transport distance is far and the speed is slow. In the process of leaf fertilization, all kinds of nutrients are quickly absorbed by crop leaves, and directly enter the plant body from the leaves to participate in the metabolism of crops. The absorption rate and fertilizer efficiency are faster than soil fertilization, and the rate of fertilizer absorption is about 1 times faster than that of the root.
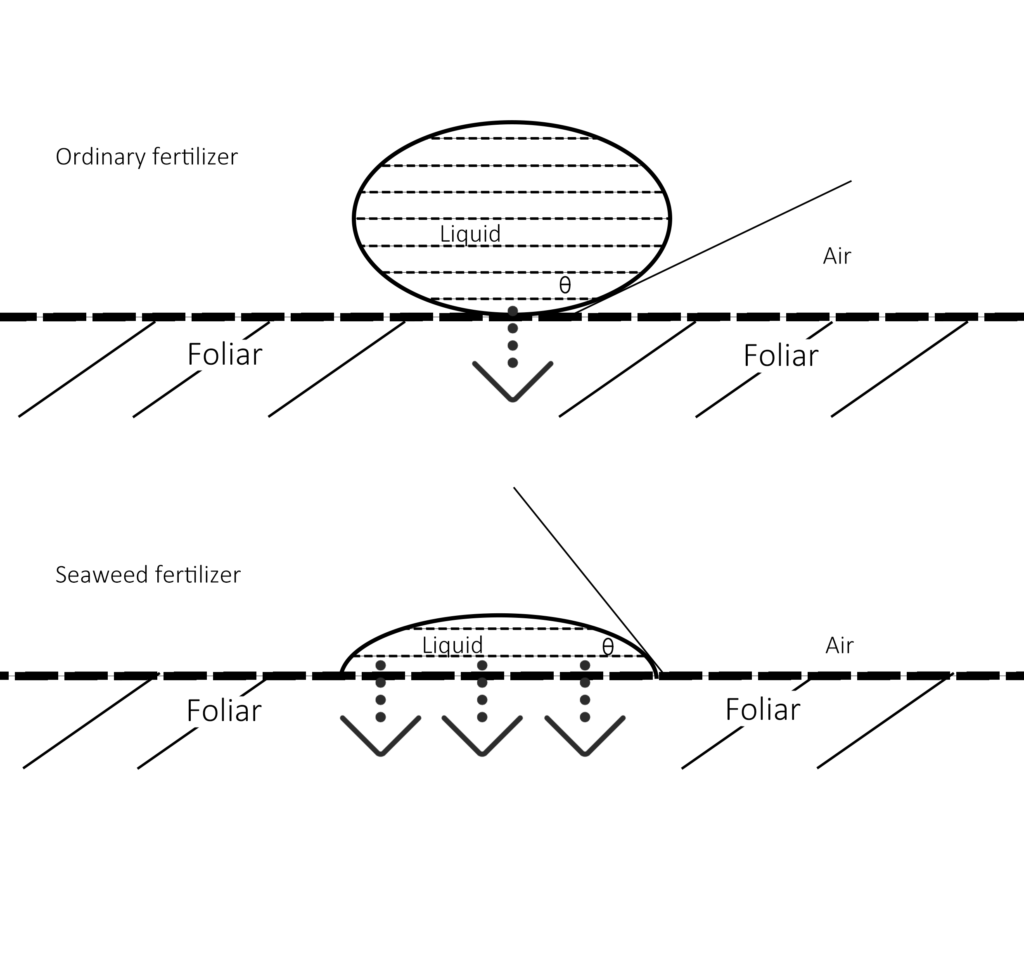
Compared with ordinary fertilizers, alginate in seaweed leaf fertilizer can reduce the surface tension of water, form a film on the surface of plant leaves, effectively increase the contact area, and facilitate water or water-soluble substances to enter the cell through the barrier structure of the leaf surface, so that plants can fully and effectively absorb nutrients.

① Fast nutrient absorption, good fertilizer effect. After soil fertilization, various nutrient elements are first adsorbed by the soil, and some fertilizers must be absorbed by crop roots through ion exchange or diffusion after a transformation process in the soil, and reach the leaves through the vascular bundles of roots and stems, in which the nutrient transport distance is far and the speed is slow. In the process of leaf fertilization, all kinds of nutrients are quickly absorbed by crop leaves, and directly enter the plant body from the leaves to participate in the metabolism of crops. The absorption rate and fertilizer efficiency are faster than soil fertilization, and the rate of fertilizer absorption is about 1 times faster than that of the root.
Compared with ordinary fertilizers, alginate in seaweed leaf fertilizer can reduce the surface tension of water, form a film on the surface of plant leaves, effectively increase the contact area, and facilitate water or water-soluble substances to enter the cell through the barrier structure of the leaf surface, so that plants can fully and effectively absorb nutrients.

① Fast nutrient absorption, good fertilizer effect. After soil fertilization, various nutrient elements are first adsorbed by the soil, and some fertilizers must be absorbed by crop roots through ion exchange or diffusion after a transformation process in the soil, and reach the leaves through the vascular bundles of roots and stems, in which the nutrient transport distance is far and the speed is slow. In the process of leaf fertilization, all kinds of nutrients are quickly absorbed by crop leaves, and directly enter the plant body from the leaves to participate in the metabolism of crops. The absorption rate and fertilizer efficiency are faster than soil fertilization, and the rate of fertilizer absorption is about 1 times faster than that of the root.
Compared with ordinary fertilizers, alginate in seaweed leaf fertilizer can reduce the surface tension of water, form a film on the surface of plant leaves, effectively increase the contact area, and facilitate water or water-soluble substances to enter the cell through the barrier structure of the leaf surface, so that plants can fully and effectively absorb nutrients.







